Building Information Modeling can be used to increase project efficiency. By improving task scheduling, more clearly delineating construction stages, communication improvements, and pinpointing prefabricated areas – BIM provides a great way to optimize construction projects. In fact,this technology can offer real-time updates and streamline workflows, ultimately minimizing resource wastage. Moreover, by identifying potential issues in the planning phase, BIM effectively reduces costly on-site revisions and rework.
Architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries have long sought methods of reducing costs, increasing productivity, and speeding up project delivery times. BIM can assist these efforts by creating an accurate virtual construction site model. This digital twin allows for predictive analysis, providing insights into possible outcomes and aiding in making informed decisions. Furthermore, the interactive nature of a BIM model aids in improving stakeholder communication and understanding, leading to better coordination and ultimately, to successful project completion.
Page Contents
Cost Savings
Traditional designs for buildings and structures use two-dimensional plans and drawings, which are converted to 3D models for project stakeholders to visualize dimensions and requirements more precisely. This approach has the potential for cost savings through reduced change orders, decreased risks, and the elimination of delays.
During the pre-design stage, general contractors (GCs) and architects can use BIM models of various design options to help an owner select the most suitable option that meets their needs. Furthermore, they can generate cost estimates using BIM – saving both time and money by eliminating the need to enter this information multiple times into different scheduling and costing programs.
BIM models can help project teams coordinate, size, and space items efficiently while decreasing time spent resolving conflicts. In addition, these models can generate fabrication/shop drawings that speed up construction.
Time Savings
Building Information Modeling helps streamline the design and construction process by facilitating collaborative work among project team members. By simultaneously eliminating multiple documents with multiple stakeholders, BIM decreases time spent managing and revising documents while increasing efficiency by eliminating manual counting of components.
BIM can save time during the design and preconstruction phases by helping teams produce accurate cost estimates and material inventories, resolve conflicts quickly, identify any delays to a project’s completion quickly, and identify issues that might impede it.
BIM models can help to guide projects from their inception through deconstruction. According to surveys of AEC industry participants, using BIM techniques has increased productivity, reduced costs, and shortened schedules; they may also be utilized to perform code compliance and facility management duties, reducing delays in costly project completions.
Environmental Impact
BIM can assist projects in mitigating the environmental impact they have on nature. Decreasing demand for raw materials and fossil fuels can reduce air pollution emissions that cause respiratory ailments in humans and damage ecosystems worldwide dimensions.
Furthermore, this approach to modeling complex spatial relationships provides various benefits to AEC industry players, including increased profitability, decreased costs, and shorter project durations – it can even facilitate greater customer-contractor collaboration!
Collaboration
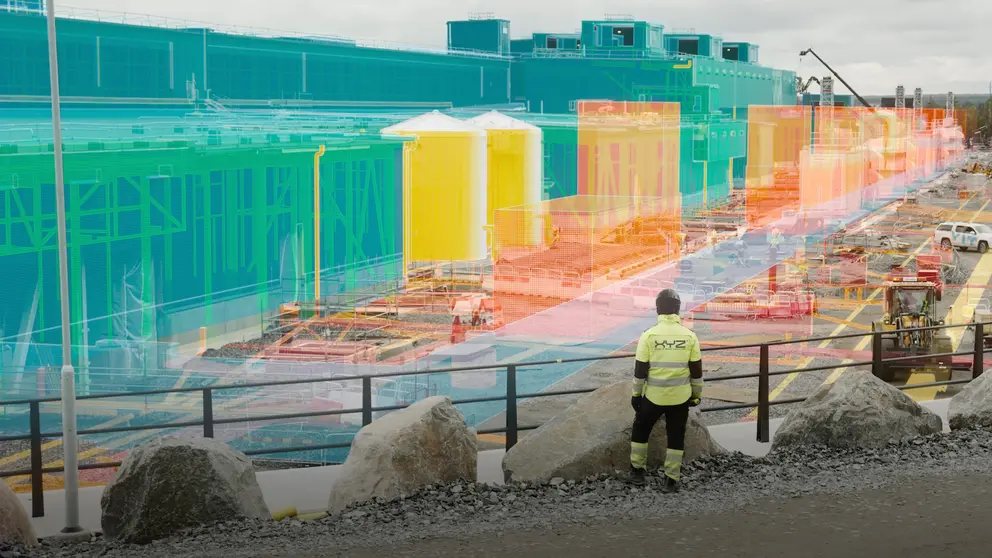
BIM can be utilized during the construction phase to digitally construct an accurate virtual model of a building and manage data such as infrastructure, materials, and assemblies. Once finished, facility managers can also utilize this model for operations and maintenance – for instance, monitoring an air-handling unit’s performance.
BIM collects project information into a central database that all stakeholders can access throughout its lifespan. This approach benefits project owners, engineers, and other key personnel by helping them work collaboratively to anticipate any design or construction difficulties and identify any potential stumbling blocks early on in a project’s lifespan.
BIM allows teams to visualize projects before construction begins, which reduces risks and enhances communication, leading to higher quality, reduced costs, and fewer problems on-site, as well as making the transition into building operation and maintenance more straightforward.
Risk Management
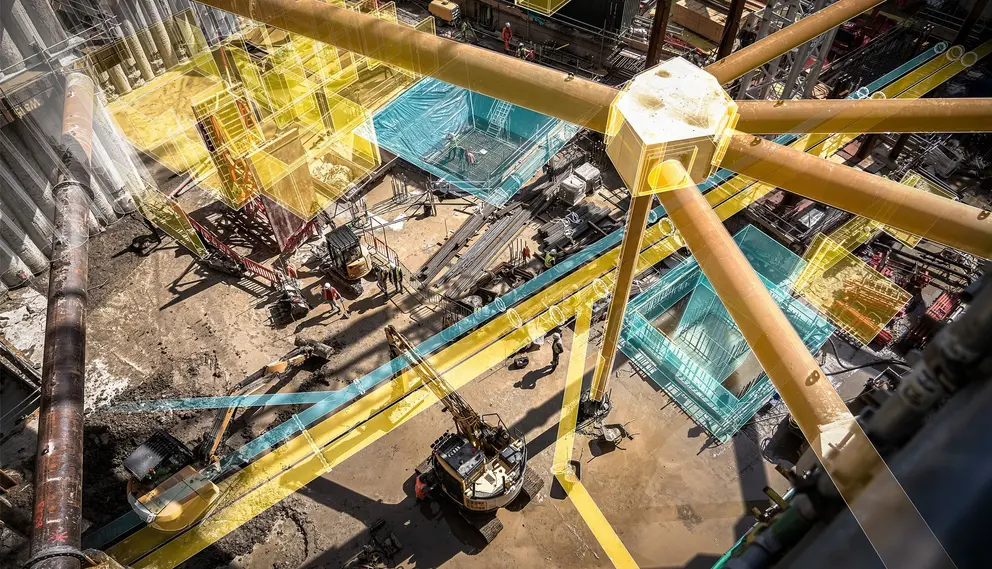
Building Information Modeling (BIM) revolutionizes risk management in project execution. BIM provides a virtual representation of the project, allowing for detailed scrutiny even before the initiation of the construction phase. This enables project managers to identify potential risks associated with design flaws, safety hazards, constructability issues, and any potential conflicts in resources.
It’ is crucial to mitigate risks in construction as early as possible, given the high cost of errors in this field. With BIM, risk scenarios can be modeled and evaluated, allowing preventive measures to be taken beforehand. Furthermore, BIM makes it possible to simulate different strategies and solutions, thus fostering proactive decision-making. Risk management is, therefore, more effective with BIM, making projects safer and more reliable.
Quality Control
BIM also plays a significant role in improving the quality of construction projects. Utilizing BIM technology, project managers can achieve a high level of accuracy and precision in their projects. With its 3D visualizations, BIM gives a clear understanding of the project from the outset, allowing for meticulous planning and design, which directly translates to quality enhancement.
This is not all. Building Information Modeling also helps ensure that the project adheres to the specified standards and building codes. With its ability to detect inconsistencies and errors in the design stage, BIM prevents potential issues from becoming costly construction problems. It ensures that every aspect of the project is thoroughly planned, designed, and executed, leading to improved quality and performance of the final product.
The effective utilization of advanced technology, data analysis, cost estimation, risk assessment, and stakeholder collaboration are crucial elements in achieving successful construction optioneering within the context of applying Building Information Modeling (BIM) in project management.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers an innovative and effective way to manage construction projects. The application of BIM results in cost and time savings, reduces the environmental impact of construction, fosters improved collaboration, enhances risk management, and promotes quality control.
BIM is not just a tool for visualizing a project; it is a powerful solution for managing, controlling, and executing the entire lifecycle of a project. It creates a collaborative and integrated environment that enables stakeholders to work together more effectively, making the construction process more efficient and less prone to errors.
Embracing this techn is not only beneficial for project management teams but is also a strategic move towards sustainable, efficient, and high-quality construction practices. The potential benefits of BIM are vast and wide-ranging, and as the technology continues to mature, we can expect to see its influence in the construction industry deepen, offering further advancements and improvements in project management.